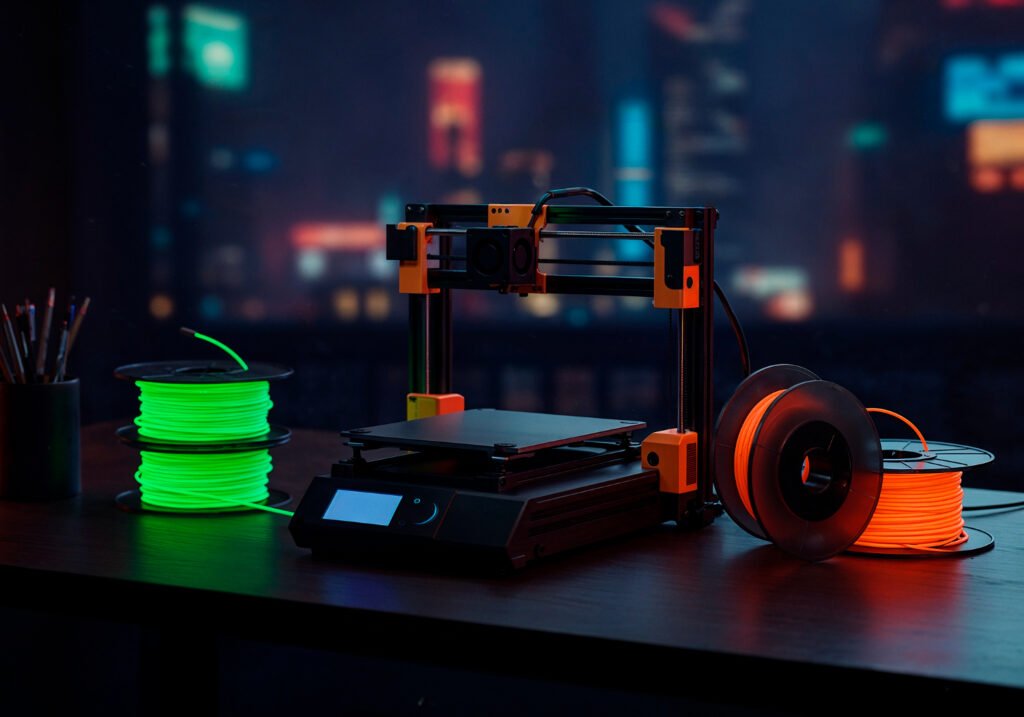
In today’s fast-paced industries, prototyping plays a critical role in turning creative concepts into tangible outcomes. By bridging the gap between ideas and production, it allows innovators to test, refine, and validate their designs before committing to full-scale manufacturing.
Through modern prototype design and advanced development services, businesses can explore multiple iterations quickly and cost-effectively. Whether using traditional methods or creating a 3D-printed model, the ability to build functional representations accelerates decision-making and reduces the risk of costly mistakes.
Ultimately, this process empowers startups, engineers, and established companies alike to bring products to life with confidence—making prototyping one of the most valuable tools in modern innovation.
What Is prototyping and Why It Matters
At its core, this approach transforms an abstract idea into a physical or digital model that can be tested and refined. It acts as a bridge between creative concepts and final products, giving teams the opportunity to identify design flaws, improve usability, and validate functionality before investing in large-scale production.
Modern prototype design goes beyond sketches and CAD files. It includes physical models created through manufacturing techniques such as CNC machining, injection molding, or rapid 3D printing, as well as digital simulations and virtual models used for early validation. These methods enable businesses to gather feedback, test performance, and shorten development cycles.
For both startups and established enterprises, working with professional design and manufacturing partners reduces risk and saves costs. By identifying issues early, this development stage ensures innovations move forward with greater confidence and efficiency—an essential advantage in today’s competitive product landscape.
Types of Prototypes You Should Know About
e purpose. Depending on the stage of development, businesses and innovators can rely on different forms of prototype design to validate ideas and guide decision-making.
Concept prototypes are very early representations, often simple sketches, mock-ups, or rough 3D shapes. They are not intended for performance testing but help communicate ideas clearly to stakeholders.
Functional prototypes take development a step further by allowing teams to test usability and core features. These models are commonly produced through manufacturing techniques such as CNC machining or rapid 3D printing, enabling hands-on evaluation.
High-fidelity prototypes closely resemble the final product in both appearance and performance. Often created by specialized manufacturing companies or advanced development services, they are essential for investor presentations, user testing, and pre-production validation.
By leveraging the right type of model at the right time, businesses reduce risk, save costs, and accelerate the path from idea to product.
How Prototyping Reduces Risk and Saves Money
Effective prototyping is more than just building early models—it is a strategy to minimize costly mistakes and accelerate decision-making. By creating tangible models through prototype design and manufacturing processes, teams can test functionality, identify weak points, and correct flaws before full-scale production. This early validation helps avoid expensive design errors that might otherwise surface late in the process.
Modern development services also make it possible to build quick iterations using methods like CNC machining or a 3D print prototype, giving innovators the flexibility to compare different options at low cost. This not only reduces financial risk but also speeds up the approval process for stakeholders and investors who want evidence before committing resources.
Whether working with startups or established enterprises, trusted prototype manufacturing companies ensure that innovations move forward with confidence, saving both time and money in today’s competitive product landscape.
Tools and Technologies Behind Prototyping
Modern prototyping uses a wide range of tools and technologies to help innovators turn ideas into testable, functional products. Each tool has its unique strengths, depending on whether the goal is concept validation, functional testing, or preparing for production.
3D Printing: One of the fastest and most cost-effective ways to create early models. A 3D print prototype allows teams to test shapes, geometries, and even assembly fit without the need for expensive tooling.
CNC Machining: Essential when accuracy, strength, and real-world performance are required. CNC is widely used in manufacturing processes for both metals and plastics, producing functional parts with tight tolerances.
Virtual Prototyping and Digital Simulations: A risk-free method to test product performance digitally. By running stress tests, usability studies, and simulations, businesses can refine designs before investing in physical models.
Injection Molding for Prototypes: Known as rapid or bridge tooling, this process creates low-volume parts in production-grade materials. It’s often used by manufacturing companies for consumer products and medical devices.
Sheet Metal Prototyping: Ideal for enclosures, brackets, and structural parts. This method offers quick turnaround for functional metal models that resemble end-use parts.
Laser Cutting & Waterjet Cutting: Precise processes to quickly create 2D components from metal, wood, or plastic. These are popular in early development services when flat parts or quick mock-ups are needed.
Foam, Clay, or Wood Models: Still used in industrial design for concept development, allowing teams to visualize scale and ergonomics in the earliest stages.
By combining these technologies—or using them through specialized manufacturing companies—businesses reduce risk, save costs, and accelerate the journey from idea to product.
Prototyping in Action: Real-World Examples
The true value of prototyping is best seen in real-world applications, where innovative ideas are transformed into functional products across different industries.
Medical Industry: In healthcare, precision and safety are critical. Through advanced prototype design and manufacturing expertise, companies develop surgical instruments, dental tools, and implants that must meet strict standards. Using methods like CNC machining or a 3D print prototype, medical teams can validate ergonomics and functionality before large-scale production, reducing risks for patients.
Automotive Industry: Car manufacturers and suppliers rely heavily on development services to test engine components, body panels, and interior parts. Rapid manufacturing partners enable them to check durability, aerodynamics, and fit, ensuring that final designs meet both performance and safety requirements.
Startups and Entrepreneurs: For new ventures, prototyping is the fastest way to transform a concept into something tangible that can attract investors. Whether built through 3D print prototypes for early demos or CNC-machined parts for functional testing, early models help startups validate ideas quickly and secure funding.
Future of Prototyping: Where Innovation Is Heading
The future of prototyping is being reshaped by breakthroughs in artificial intelligence, sustainable materials, and the fusion of digital and physical workflows. These innovations are redefining how prototype design, prototype manufacturing, and prototyping services will operate in the coming decade.
- AI in Design and Simulation: According to McKinsey’s Future of Manufacturing 2024, integrating AI into CAD modeling and simulations is expected to shorten design cycles by up to 30%. This trend builds on findings from Nature Machine Intelligence (2022), which showed how generative AI can automatically create and optimize design iterations, while predictive algorithms enhance stress testing before physical prototype manufacturing.
- Smart and Sustainable Materials: Deloitte Insights 2024 – Sustainable Manufacturing reports that more than 40% of global manufacturers aim to adopt bio-based and recyclable polymers in their prototyping services by 2030. This aligns with research in Advanced Materials (2023), which highlights the development of high-performance composites and resins suitable for both 3D print prototypes and CNC machining.
- Hybrid Digital + Physical Prototyping: Gartner’s Emerging Tech Report 2024 predicts that by 2027, nearly 70% of prototype manufacturing companies will use digital twins to validate designs before building physical prototypes. This evolution is reinforced by studies in IEEE Access (2022), which documented the efficiency of linking virtual simulations with physical prototyping for faster and more accurate development.
Together, these advances point toward a smarter, greener, and more integrated era of prototyping, where businesses can innovate faster while meeting global demands for sustainability and precision.
Conclusion: Prototyping as the Foundation of Innovation
From concept sketches to fully functional models, prototyping is the foundation of modern innovation. It reduces risk, saves costs, and accelerates the journey from idea to market—empowering startups, engineers, and global enterprises alike to innovate with confidence. By combining prototype design, prototype manufacturing, and cutting-edge prototyping services, businesses can validate ideas and move forward faster than ever before.
At Netprocore, we simplify this process by offering end-to-end solutions, from 3D print prototypes to CNC machining and engineering support. Whether you need a quick model for testing or a high-fidelity prototype for investors, our team delivers precision, speed, and reliability.
Explore how Netprocore can bring your ideas to life—partner with us and take the next step toward smarter product development.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How CAD Design Works: From Concept to Digital Model
At its core, CAD design transforms a creative concept into a precise digital model through a structured process that blends creativity with engineering logic. It begins with a simple idea or sketch, which is then refined using advanced CAD designing software such as AutoCAD, SolidWorks, or Fusion 360. These tools enable designers to convert two-dimensional drawings into three-dimensional geometries with pinpoint accuracy.
The process involves several key stages. Geometry modeling defines the shape and structure of a part, while parameterization allows for flexible modifications by linking dimensions and constraints—so changing one feature automatically updates the entire design. 3D visualization then brings the model to life, allowing teams to explore every angle, material, and assembly interaction before production.
Beyond visualization, CAD design supports simulation and testing in a digital environment. Engineers can analyze stress, temperature, and motion to predict how a part will perform in real-world conditions. This digital validation, especially when combined with cad software for 3D printing, shortens development time and reduces costly errors.
Ultimately, professional CAD design services streamline this entire process—turning raw ideas into manufacturable digital prototypes that bridge the gap between imagination and production.
Types of CAD Design and Applications Across Industries
Modern CAD design encompasses several distinct categories, each serving a specific role in the engineering and manufacturing process. Understanding these types helps businesses choose the right approach for their product development needs.
2D Drafting:
This is the foundation of all CAD design work. Using software such as AutoCAD, designers create precise technical drawings, schematics, and blueprints that define dimensions and tolerances. Although primarily flat, 2D drafting remains essential in architecture, civil engineering, and electronics for layout and documentation.
3D Modeling:
With the evolution of CAD designing software, 3D modeling has become the industry standard. It enables engineers to create detailed virtual models of parts or assemblies, visualize geometry, and simulate motion or interference. 3D models also serve as the base files for CAD software for 3D printing, bridging digital design and physical manufacturing.
Simulation and Rendering:
This advanced stage of CAD design uses physics-based simulations and photorealistic rendering to test how a product will perform or appear before production. Engineers can analyze stress, airflow, and temperature behavior, while designers can produce life-like visualizations for client presentations and marketing.
Across industries, these CAD applications drive innovation:
- Automotive & Aerospace: Design of engines, body structures, and aerodynamic components.
- Architecture: Planning and visualization of buildings and infrastructure.
- Medical Devices: Modeling prosthetics, implants, and surgical instruments.
- Consumer Products: Developing ergonomic, aesthetic, and functional designs.
From concept to production, professional CAD design services unify these capabilities—helping companies innovate faster, reduce errors, and ensure precision across every stage of product development.
Top CAD Designing Software Used by Engineers
Choosing the right CAD designing software is one of the most important decisions for engineers, product designers, and manufacturers. Each program offers unique features that cater to specific industries, workflows, and project scales. Here are some of the most widely used tools in CAD design today.
1. AutoCAD – The Industry Standard
Developed by Autodesk, AutoCAD remains one of the most popular and versatile CAD tools worldwide. It’s ideal for 2D drafting and basic 3D modeling, offering precision and compatibility across architecture, civil engineering, and manufacturing. AutoCAD’s layer management, annotation tools, and DWG file support make it the backbone of digital drafting.
2. SolidWorks – Mechanical Design and Simulation Powerhouse
Created by Dassault Systèmes, SolidWorks specializes in mechanical and industrial CAD design. Engineers use it for parametric modeling, motion analysis, and stress simulation, making it perfect for product development, machinery, and complex assemblies.
3. Fusion 360 – Cloud-Based Collaboration
Autodesk Fusion 360 integrates design, simulation, and manufacturing in one platform. Its cloud-based approach allows real-time collaboration between engineers and clients. It’s also widely used for cad software for 3D printing, since it can export STL files and simulate printability directly from the design.
4. CATIA – Aerospace and Automotive Engineering Leader
CATIA, another Dassault Systèmes product, is the gold standard for large-scale engineering projects in aerospace, automotive, and industrial equipment. It supports advanced surface modeling, systems engineering, and multi-physics simulations, which make it indispensable for high-precision industries.
5. TinkerCAD / FreeCAD – Simplicity for Learning and Rapid Prototyping
For beginners and makers, TinkerCAD and FreeCAD provide easy-to-learn interfaces for conceptual modeling and 3D print prototypes. They are commonly used in education, hobbyist projects, and early-stage CAD design services.
From entry-level to enterprise-grade platforms, these CAD designing software tools shape the modern world of engineering — helping professionals visualize, validate, and manufacture products faster and more efficiently.
CAD Design for 3D Printing: Bridging Digital and Physical Worlds
In modern manufacturing, CAD design plays a crucial role in bridging the gap between digital modeling and physical production. Every 3D-printed object begins as a precise digital file created using advanced CAD designing software such as AutoCAD, Fusion 360, or SolidWorks. These platforms allow engineers to visualize complex geometries, define tolerances, and prepare models optimized for additive manufacturing.
The process typically starts with creating or importing a 3D model, which is then exported into a printable file format such as STL (Stereolithography) or OBJ (Object File). These formats contain the mesh and surface geometry required by 3D printers to interpret the design layer by layer. However, unlike traditional machining, 3D printing imposes unique limitations—such as minimum wall thickness, overhang angles, and support structures—that must be addressed during CAD design.
By leveraging specialized cad software for 3D printing, engineers can adjust designs for manufacturability, simulate build orientation, and ensure structural stability before printing. Professional CAD design services, like those offered by Netprocore, take this process even further—combining expert modeling with real-world printing expertise to deliver ready-to-produce digital files. Whether for rapid prototyping or end-use components, CAD design ensures that every printed part meets both aesthetic and functional expectations, truly connecting the digital and physical worlds.
CAD Design for 3D Printing: Bridging Digital and Physical Worlds
In modern manufacturing, CAD design plays a crucial role in bridging the gap between digital modeling and physical production. Every 3D-printed object begins as a precise digital file created using advanced CAD designing software such as AutoCAD, Fusion 360, or SolidWorks. These platforms allow engineers to visualize complex geometries, define tolerances, and prepare models optimized for additive manufacturing.
The process typically starts with creating or importing a 3D model, which is then exported into a printable file format such as STL (Stereolithography) or OBJ (Object File). These formats contain the mesh and surface geometry required by 3D printers to interpret the design layer by layer. However, unlike traditional machining, 3D printing imposes unique limitations—such as minimum wall thickness, overhang angles, and support structures—that must be addressed during CAD design.
By leveraging specialized cad software for 3D printing, engineers can adjust designs for manufacturability, simulate build orientation, and ensure structural stability before printing.
Professional CAD design services, like those offered by Netprocore, take this process even further—combining expert modeling with real-world printing expertise to deliver ready-to-produce digital files. Whether for rapid prototyping or end-use components, CAD design ensures that every printed part meets both aesthetic and functional expectations, truly connecting the digital and physical worlds.
CAD Design Services: Why Businesses Outsource Digital Modeling
In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, many companies are turning to professional CAD design services instead of managing design work in-house. The reason is simple: outsourcing offers access to specialized expertise, advanced tools, and faster project delivery—all while reducing costs and improving product quality.
By partnering with firms that specialize in CAD design, businesses gain the advantage of working with engineers proficient in multiple CAD designing software platforms such as AutoCAD, SolidWorks, and Fusion 360. This ensures compatibility across industries, from architecture to aerospace, and allows complex designs to be developed and refined with exceptional precision.
Outsourcing CAD design services also helps companies scale efficiently. Rather than investing in expensive software licenses, training, and full-time designers, they can rely on external teams for on-demand modeling, simulation, and cad software for 3D printing optimization. This flexibility accelerates product development and reduces time-to-market.
Companies like Netprocore go a step further by offering integrated CAD and prototyping solutions—turning digital models into physical products through advanced 3D printing, CNC machining, and simulation. Whether for concept validation or production-ready models, outsourcing CAD design empowers businesses to innovate smarter, faster, and more cost-effectively.
The Future of CAD Design
The next generation of CAD design is evolving beyond static modeling — it’s becoming intelligent, connected, and predictive. Emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), cloud computing, and digital twins are transforming how engineers design, test, and manufacture products.
AI-Powered CAD and Generative Design
Artificial intelligence is changing how products are conceived and optimized. Modern CAD designing software, such as Autodesk Fusion 360 and PTC Creo, now integrates generative design — an AI-driven process that automatically creates thousands of design options based on performance goals, material constraints, and cost targets. Engineers no longer draw every line manually; instead, they guide algorithms that learn and improve from real-world data.
Cloud-Based CAD Collaboration
With the rise of global engineering teams, cloud-based CAD design services are enabling real-time collaboration across continents. Platforms like Onshape and Fusion 360 allow multiple users to work simultaneously on a single model, eliminating version conflicts and accelerating design-to-production cycles. This approach also enhances data security and remote accessibility — key priorities for modern manufacturing.
Digital Twins and Smart Manufacturing
A major leap in CAD design is its integration with digital twin technology — virtual replicas of real products or systems. Using live sensor data and simulation feedback, companies can monitor, test, and improve product performance throughout its lifecycle. Siemens and Dassault Systèmes have already demonstrated how digital twins connect CAD designing software with manufacturing execution systems, creating a fully integrated product ecosystem.
As CAD design continues to evolve, the fusion of AI, cloud, and digital simulation is set to redefine how innovation happens faster, smarter, and more sustainable than ever before.
Conclusion: How CAD Design Powers the Future of Modern Engineering
In today’s era of digital transformation, CAD design stands as the foundation of modern engineering. From conceptual sketches to production-ready models, CAD enables innovation that is faster, smarter, and more precise than ever before. It bridges creativity with technical accuracy—allowing engineers, architects, and manufacturers to bring ideas to life with unmatched efficiency.
Without CAD designing software and advanced CAD design services, the speed and precision we associate with modern product development would simply not be possible. Through tools like AutoCAD, SolidWorks, and Fusion 360, industries can visualize, simulate, and optimize every detail long before production begins.
At Netprocore, we make this digital power accessible. Our comprehensive CAD design services combine engineering expertise with cutting-edge technology—from cad software for 3D printing to full-scale digital prototyping. Whether you’re designing your first concept or refining a complex assembly, Netprocore provides the accuracy, collaboration, and agility needed to turn ideas into reality.

Prototyping is the process of creating physical or digital models to test and refine ideas before full-scale production. It helps reduce risks, identify design flaws early, and accelerate time-to-market, making it an essential step in modern product development.
The most widely used methods include 3D print prototypes for quick and affordable models, CNC machining for precision parts, injection molding for low-volume production in real materials, and digital simulations for virtual testing.
By catching design issues early, prototyping services help companies avoid costly mistakes during mass production. Iterations are faster and cheaper, especially when using methods like 3D printing or CNC machining, ensuring smarter investment decisions.
- Sectors like medical devices, automotive, aerospace, consumer electronics, and startups all rely on prototype manufacturing companies. Prototyping enables them to validate functionality, improve usability, and present investor-ready models.
Netprocore offers end-to-end prototype design and prototype manufacturing solutions, including 3D printing, CNC machining, CAD engineering, and post-processing. Whether you need a quick demo model or a high-fidelity prototype, Netprocore delivers speed, accuracy, and reliability.